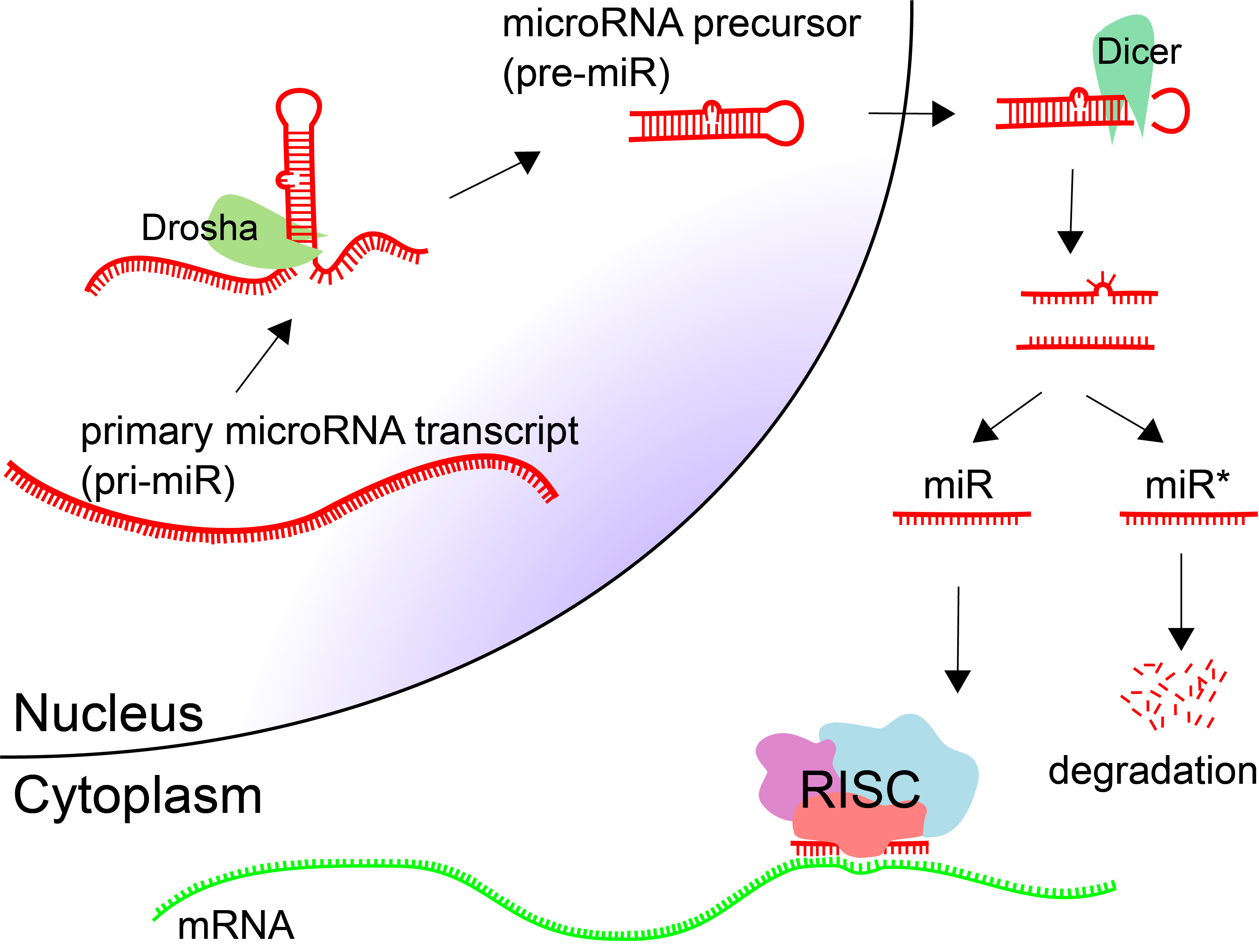
MicroRNA, a groundbreaking discovery unveiled by Nobel laureate Gary Ruvkun and his colleague Victor Ambros in 1992, has transformed our understanding of gene regulation. Initially observed in the simple roundworm C. elegans, these tiny RNA molecules now play an essential role in controlling gene expression across many life forms, including humans. Their significance was initially lost on the scientific community, which failed to recognize the revolutionary implications of microRNAs for biology and medicine. Thanks to continuous support from NIH funding, this area of research has burgeoned, and microRNAs are currently being explored in clinical trials for a range of diseases, including cancer and Alzheimer’s. As interest in this field grows, it highlights how essential microRNA is to the future of therapeutic innovations and gene therapy.
Small non-coding RNA molecules, known as microRNA, have presented a remarkable insight into the dynamics of gene expression and regulation. This novel paradigm in molecular biology stems from early investigations by renowned scientist Gary Ruvkun, who, alongside Victor Ambros, uncovered their intricate roles in the C. elegans model. Initially, the potential of these small RNA segments was not duly acknowledged, yet they have since emerged as crucial elements in regulating genes across species, driven largely by sustained NIH investments. The growing body of research has led to exciting therapeutic approaches for various conditions, such as cancer and neurological disorders. Today, researchers are increasingly recognizing these tiny regulators as foundational players in the intricate web of genetic control.
The Revolutionary Discovery of microRNA
The discovery of microRNA by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros in 1992 marked a pivotal moment in the field of gene regulation. Initially, their findings, published in the esteemed journal Cell in 1993, did not garner immediate recognition within the broader scientific community. However, as additional research unfolded, it became clear that microRNAs played a crucial role in regulating genes not just in the C. elegans model organism, but also in humans and other species. This realization has since transformed our understanding of genetic regulation and has initiated significant advancements in molecular biology.
Today, microRNAs are no longer seen as mere curiosities but as fundamental components of gene expression regulation. Their ability to modulate protein production is critical in various biological processes, linking back to Ruvkun and Ambros’s initial discoveries. The groundbreaking nature of this research laid the groundwork for the therapies currently in clinical trials for a range of diseases, including cancer and heart disease. Our current understanding of microRNA reveals approximately 1,000 such molecules within the human genome alone, regulating a significant portion of our protein-coding genes.
Impact of Federal Funding on Scientific Research
Gary Ruvkun’s research journey, spanning over four decades, has been heavily supported by federal funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). This financial backing has not only been a lifeline for his laboratory but has also played a vital role in fostering innovation within the field of genetics. Ruvkun’s experience highlights a critical point: substantial NIH funding has equipped researchers with the financial means to explore groundbreaking avenues in science, leading to discoveries that have transformed entire industries, such as pharmaceutical development.
Despite Ruvkun’s success, he voices concerns regarding potential cuts to federal funding. He argues that reducing financial support could dissuade young scientists from pursuing careers in research, as evidenced by the uncertainty faced by lab members about their future in the field. The federal commitment to scientific research has historically catalyzed advancements in technology and medicine, contributing to the United States’ position as a leader in global science and innovation. Ruvkun’s appeal for sustained investment underscores the importance of fostering an environment where scientific inquiry can flourish.
MicroRNA Therapies in Clinical Trials
The strides made in understanding microRNA have led to the development of innovative therapies currently in clinical trials. Researchers are exploring their potential in treating conditions such as heart disease, cancer, Alzheimer’s, and Crohn’s Disease, showcasing the significant implications of this research. The ability of microRNAs to regulate gene expression presents a unique opportunity for target-specific therapies, which could greatly enhance treatment efficacy while minimizing side effects.
Investments in this area are expected to continue increasing as the understanding of microRNAs deepens. The anticipation surrounding the outcomes of these clinical trials reflects a larger trend in molecular medicine, where genetic insights are directly translated into therapeutic applications. As researchers harness the power of microRNAs, the landscape of treatment for various genetic and degenerative diseases is poised for groundbreaking changes, underscoring the importance of foundational research supported by grants.
The Evolution of Gene Regulation Understanding
Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros’s discovery of microRNA has significantly reshaped our understanding of gene regulation. Before their work, the complexity of gene expression was not fully appreciated, leading to a limited comprehension of how genes operated at a molecular level. Their findings introduced a new frontier in the study of genetics, highlighting the intricate ways in which these tiny RNA molecules modulate gene activity across different organisms, setting the stage for future breakthroughs in biology.
As interest in this field grew, researchers began to realize that microRNAs serve crucial functions beyond C. elegans, operating similarly across plants and animals. This interconnectedness has spurred a wave of research aiming to unravel the multifaceted roles of microRNAs in development and disease. The broader implications of this research suggest that by understanding gene regulation through the lens of microRNA, scientists can develop more effective genetic therapies that could revolutionize medicine.
Ruvkun’s Legacy and Influence on Molecular Biology
Gary Ruvkun’s contributions to molecular biology extend beyond his initial discovery of microRNA; he has become an influential figure in the field. His research has not only advanced our understanding of gene regulation but has also inspired countless scientists to explore this critical area of genetics. Ruvkun’s dedication to foundational research is evidenced by his commitment to training young scientists, many of whom carry forward the legacy of innovation and inquiry in their own work.
The emergence of companies like Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, which focuses on RNA interference therapies, stands as a testament to the long-term impact of Ruvkun’s research. As these cutting-edge therapeutics continue to evolve, they promise to redefine treatment methodologies for genetic diseases and demonstrate the far-reaching consequences of federally funded research. Ruvkun’s work underscores the importance of supporting scientists who challenge existing paradigms and engage in transformative research.
The Role of NIH in Advancing Science
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has played a crucial role in supporting the research endeavors of scientists like Gary Ruvkun. As a primary source of funding for biomedical research, the NIH has been instrumental in laying the foundation for groundbreaking discoveries, including the pivotal work surrounding microRNA. The significantly funded projects have enabled researchers to investigate complex biological questions, leading to advancements that benefit society at large through improved therapies and medical innovations.
Continued investment from the NIH is essential to maintain momentum in the scientific community. As demonstrated by Ruvkun’s experience, a stable funding environment fosters a culture of exploration and discovery, encouraging young scientists to pursue careers in research. By backing innovative research initiatives, the NIH not only supports individual scientists but also contributes to the overall health of the scientific landscape in the United States, ensuring the nation remains at the forefront of biomedical discovery.
The Future of Gene Regulation Research
Looking ahead, the field of gene regulation is on the cusp of significant advancements, partly fueled by the discoveries made by Ruvkun and his contemporaries. Continued exploration of microRNA will likely uncover more about their potential therapeutic applications, leading to customized treatments for various diseases. As research methods and technologies advance, scientists can expect to unravel new layers of complexity surrounding how genes interact and regulate biological processes within and across species.
Moreover, as global research efforts intensify, collaboration across borders will become increasingly important. By pooling resources and knowledge, scientists can tackle pressing health challenges with innovative solutions. The future of gene regulation research holds great promise, and with continued support from funding agencies like the NIH, the healthcare landscape may see revolutionary changes stemming from basic scientific inquiries.
Challenges in Scientific Research Funding
Despite the clear importance of federal funding in advancing scientific discovery, researchers like Gary Ruvkun express concern about ongoing challenges within the funding landscape. With fluctuations in government budgets and varying political support for science, securing stable funding has become increasingly difficult for many laboratories. These uncertainties create an environment where young scientists might hesitate to commit their careers to research, fearing unstable income and job prospects.
Addressing these challenges is vital for the sustainability of scientific innovation. A concerted effort is needed to advocate for continued and increased investment in research funding at both federal and state levels. By recognizing the long-term benefits that stem from scientific discoveries, policymakers can help ensure that the next generation of researchers is equipped to push the boundaries of knowledge and explore the complexities of gene regulation and disease treatment.
Exploring the Interconnectedness of RNA Research
The research into microRNAs has sparked a broader interest in RNA and its various roles within biological systems. This interconnectedness highlights the potential for interdisciplinary collaboration among scientists from diverse fields, including genetics, molecular biology, and computational biology. Understanding the various functions of RNA molecules could unlock further insights into gene regulation and lead to novel therapeutic approaches, expanding the horizon for medical science.
The integration of knowledge across disciplines will enable researchers to tackle complex biological questions more effectively. As scientists continue to investigate the roles of microRNA and other RNA entities, the potential for groundbreaking discoveries in understanding diseases and developing new treatment strategies becomes increasingly evident. The collaborative spirit fostered by this growing interest will likely result in innovations that surpass the original discoveries made by pioneers like Ruvkun and Ambros.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of microRNA in gene regulation?
MicroRNA plays a crucial role in gene regulation by controlling the expression of genes at the post-transcriptional level. Discovered by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros, microRNAs can regulate a large number of protein-coding genes, making them essential for various biological processes. They are involved in development, cell differentiation, and function, thereby influencing organismal behavior.
How did Gary Ruvkun contribute to our understanding of microRNA?
Gary Ruvkun, a professor at Harvard Medical School, co-discovered microRNA during his research on C. elegans. His pioneering work revealed a new layer of gene regulation that not only advanced the field of genetics but also earned him a Nobel Prize in 2024. His findings have led to significant interest in the potential of microRNAs for medical therapies.
What medical applications are currently being explored for microRNA?
Therapeutic applications of microRNA are being extensively researched, particularly for treating diseases such as heart disease, cancer, Crohn’s Disease, and Alzheimer’s. Clinical trials are underway to evaluate the efficacy of microRNAs in these conditions, showcasing their potential as a novel treatment strategy.
How did NIH funding impact the study of microRNA?
NIH funding has been pivotal to the study of microRNA, providing necessary financial support to researchers like Gary Ruvkun. This funding enabled groundbreaking research that laid the foundation for understanding microRNA’s role in gene regulation and fostered innovations in RNA-related therapies.
How are microRNA studies connected to advancements in pharmaceutical companies?
The foundational discoveries in microRNA research have propelled advancements in pharmaceutical companies, such as Alnylam, which focuses on RNA interference therapeutics. Such companies have emerged as significant players in the biotechnology sector, highlighting the transformational impact of research funded by federal agencies like the NIH.
What is the future potential of microRNA in scientific research?
The future of microRNA research is promising, with ongoing studies expected to uncover further details about their roles in gene regulation. As interest grows across different scientific disciplines, microRNAs could lead to innovations in treatments for various diseases, emphasizing their importance in modern biomedical research.
Why should we be concerned about cuts to federal funding in scientific research?
Cuts to federal funding could hinder the progress of vital research areas such as microRNA. These budget reductions could dissuade young scientists from pursuing careers in research, as evidenced by Gary Ruvkun’s concerns about the future of the scientific workforce, which relies heavily on consistent funding for advancements.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Discovery of microRNA | Made in 1992 by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros, leading to the 2024 Nobel Prize. |
| Initial Reception | The discovery was initially overlooked and was not seen as significant until later. |
| Funding Support | Research primarily funded by NIH, helping to develop a robust scientific interest over the years. |
| Clinical Applications | Therapies using microRNAs are in trials for various diseases including heart disease and cancer. |
| Impact of Research | Foundational research contributed to the growth of companies like Alnylam, demonstrating the economic benefits of federal funding. |
| Future of Scientific Research | Concerns over federal funding cuts could impact the pursuit of scientific careers for upcoming generations. |
Summary
microRNA has emerged as a crucial component in the understanding of genetic regulation and has significantly influenced the field of molecular biology. The pioneering work by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros, although initially met with skepticism, revealed vital roles of microRNAs in controlling gene expression across various species, including humans. Today, their discoveries not only advance our knowledge but also translate into innovative therapeutic strategies for diseases, solidifying microRNA’s importance in modern medicine.